In partnership with Air New Zealand’s world-class engineers, researchers across Aotearoa, New Zealand are working with NASA on a mission that will advance global understanding of the impacts of climate change.

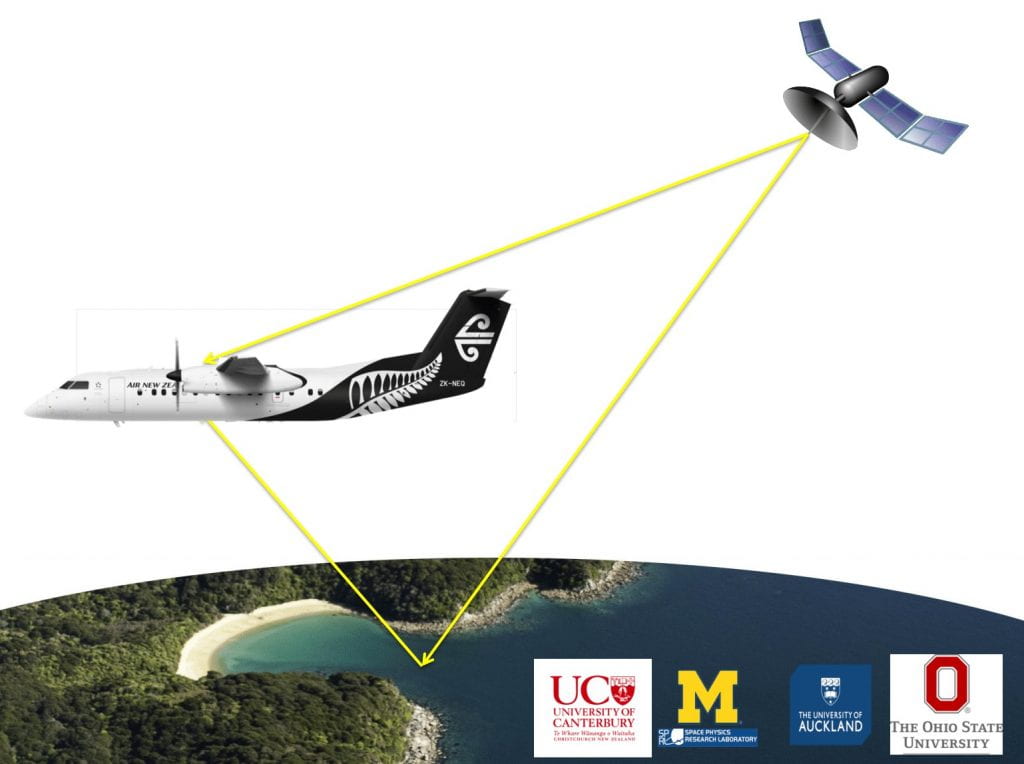
The mission, named “Rongowai” (sensing water), will see a Q300 aircraft fitted with a next-generation satellite receiver. Using GPS signals reflected from the Earth’s surface, the Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) receiver unit will act as a scientific “black box” during flights, gathering data to better predict severe storms, as well as enabling new climate change research in New Zealand. NASA will use the data that is collected and processed in New Zealand for scientific research into global water cycle processes and their interactions with climate including effects like flooding, droughts and coastal erosion.
This project has been made possible through an agreement between NASA and the New Zealand Ministry of Business, Innovation and Employment (MBIE).
How does it work?
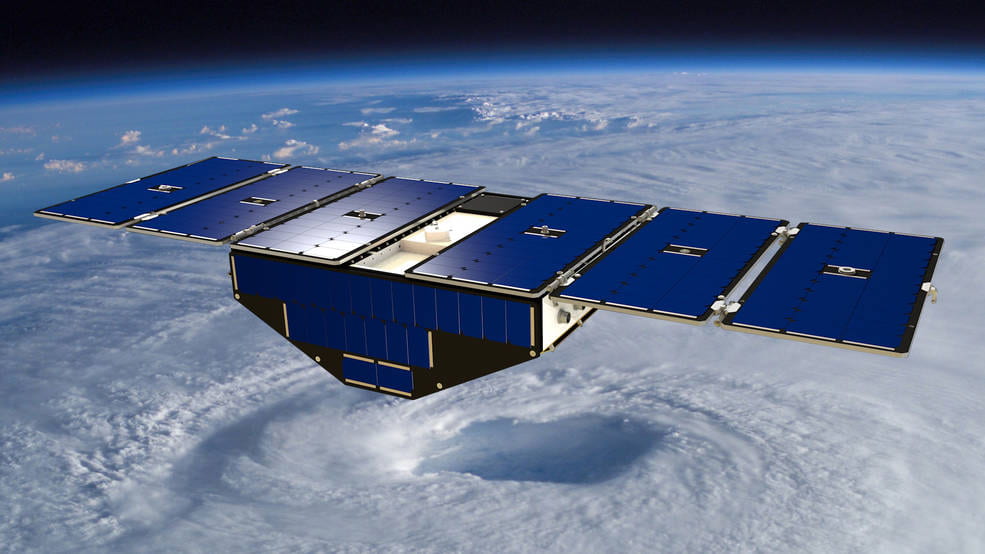
Rongowai will test a follow-on sensor for NASA’s “CyGNSS” mission, comprised of 8 Low Earth Orbiting spacecraft that receive both direct and reflected signals from GPS satellites. During each flight, the sensors on-board the Air New Zealand Q300 aircraft will record direct and reflected signals from up to 20 GNSS satellites simultaneously.

Science enablement
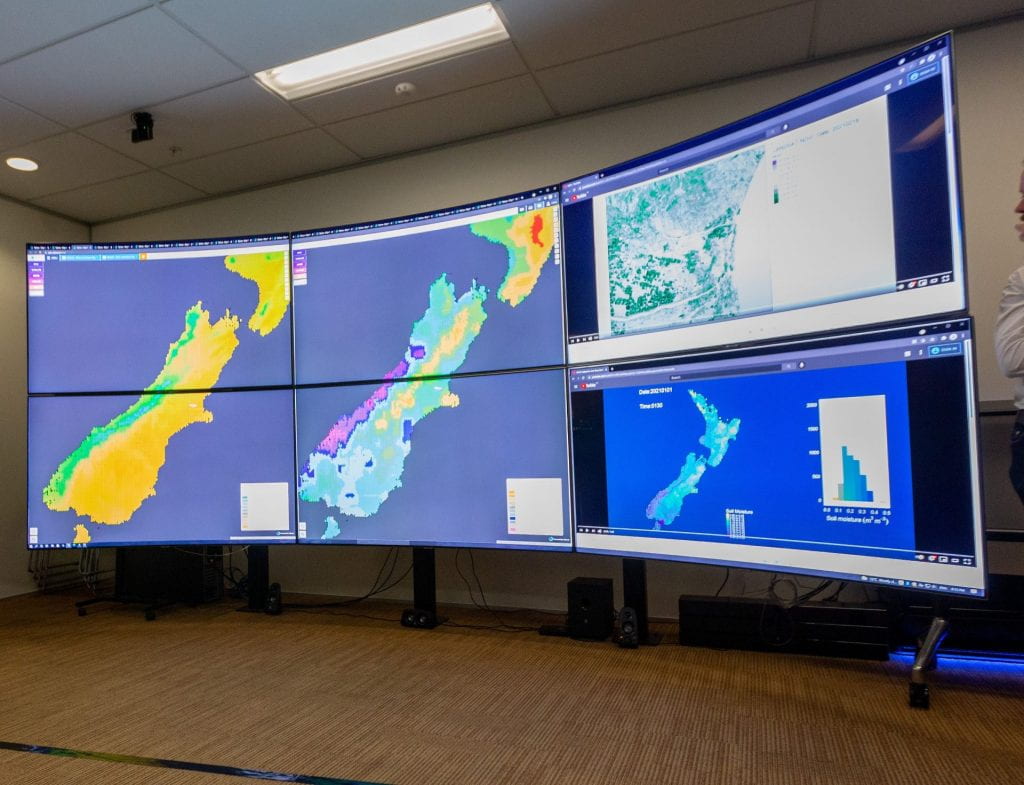
GPS signals, bounced off the ocean, will measure wind speeds and help scientists better predict cyclones and hurricanes. Over land, the technology can determine soil moisture levels, so it can also monitor climate change indicators such as drought, flooding and coastline erosion.
Meet the Team
Researchers from the University of Michigan, Ohio State University, the University of Auckland, University of Canterbury and the University Corporation for Atmospheric Research are working together on the groundbreaking Rongowai mission, with data to be hosted at University of Auckland’s Science Payload Operations Centre (SPOC).


Data
Rongowai will fly aboard Air New Zealand’s Q300 aircraft beginning in September 2022. Learn more about the data that will be collected and the link between Rongowai and NASA’s CYGNSS (Cyclone Global Navigation Satellite System) mission.







